
Vue.jsのmethods, computed, watch 演習
methods, computed, watchの違い Vue.jsには状態の扱い方として methods 、 computed 、 watch の3つの主要な […]
| 特徴 | Vuex | Pinia |
|---|---|---|
| 構成 | モジュールシステム | ストアごとに独立 |
| TypeScript | 部分的サポート | 完全サポート |
| サイズ | やや大きい | 軽量 |
| 学習曲線 | やや急 | 緩やか |
コンポーネント → (Dispatch) → アクション → (Commit) → ミューテーション → (Mutate) → ステート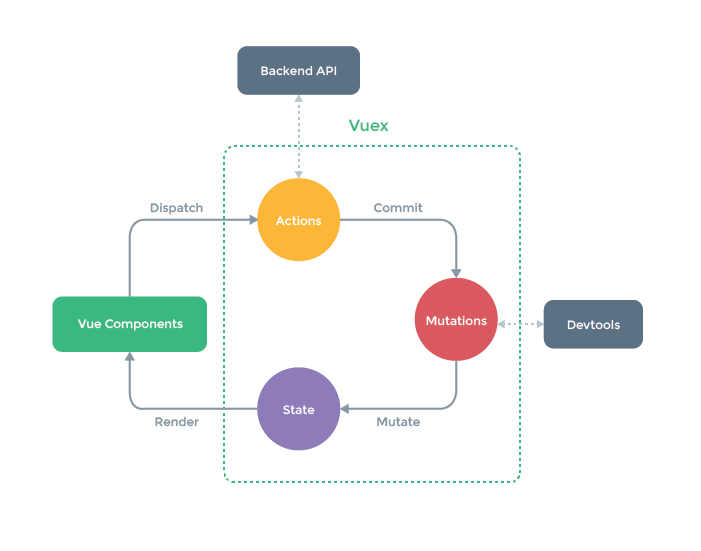
import { createStore } from 'vuex'
export default createStore({
state: {
count: 0,
todos: []
},
getters: {
doneTodos: state => state.todos.filter(todo => todo.done)
},
mutations: {
increment(state) {
state.count++
},
addTodo(state, todo) {
state.todos.push(todo)
}
},
actions: {
fetchTodo({ commit }, id) {
// 非同期処理
commit('addTodo', response.data)
}
}
})// stores/counter.js
import { defineStore } from 'pinia'
export const useCounterStore = defineStore('counter', {
state: () => ({
count: 0,
todos: []
}),
getters: {
doubleCount: (state) => state.count * 2,
doneTodos: (state) => state.todos.filter(todo => todo.done)
},
actions: {
increment() {
this.count++
},
async addTodo(todo) {
this.todos.push(todo)
}
}
})<template>
<div>
<p>カウント: {{ $store.state.count }}</p>
<!-- モジュールの場合 -->
<p>ユーザー: {{ $store.state.user.name }}</p>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
computed: {
count() {
return this.$store.state.count
}
}
}
</script><template>
<div>
<p>カウント: {{ counter.count }}</p>
<p>2倍: {{ counter.doubleCount }}</p>
</div>
</template>
<script setup>
import { useCounterStore } from '@/stores/counter'
const counter = useCounterStore()
</script>// Vuex
getters: {
expensiveProducts: state => state.products.filter(p => p.price >= 10000)
}
// Pinia
export const useProductStore = defineStore('products', {
state: () => ({
products: []
}),
getters: {
expensiveProducts: (state) => state.products.filter(p => p.price >= 10000)
}
})// Vuex
getters: {
fullNames: state => {
return state.users.map(user => `${user.lastName} ${user.firstName}`)
}
}
// Pinia
getters: {
fullNames() {
return this.users.map(user => `${user.lastName} ${user.firstName}`)
}
}// Vuex
mutations: {
increment(state, payload = 1) {
state.count += payload
}
}
// コンポーネントでの呼び出し
this.$store.commit('increment', 5)// Vuex
mutations: {
addTask(state, newTask) {
if (!newTask.title) return
state.tasks.push({
id: Date.now(),
title: newTask.title,
completed: false
})
}
}// Vuex
actions: {
async fetchUsers({ commit }) {
try {
const response = await axios.get('/api/users')
commit('setUsers', response.data)
} catch (error) {
console.error(error)
}
}
}
// Pinia
actions: {
async fetchUsers() {
try {
this.users = await axios.get('/api/users').data
} catch (error) {
console.error(error)
}
}
}// userModule.js
export default {
namespaced: true,
state: () => ({
user: null
}),
mutations: {
setUser(state, user) {
state.user = user
}
}
}
// store/index.js
import userModule from './userModule'
export default createStore({
modules: {
user: userModule
}
})// stores/user.js
import { defineStore } from 'pinia'
import { useAuthStore } from './auth'
export const useUserStore = defineStore('user', {
state: () => ({
profile: null
}),
actions: {
async fetchProfile() {
const auth = useAuthStore()
if (!auth.isLoggedIn) return
this.profile = await fetchUserProfile(auth.userId)
}
}
})// Vuexプラグイン
const localStoragePlugin = store => {
store.subscribe((mutation, state) => {
localStorage.setItem('vuex-state', JSON.stringify(state))
})
}
// 初期状態読み込み
const savedState = localStorage.getItem('vuex-state')
const store = createStore({
state: savedState ? JSON.parse(savedState) : initialState,
plugins: [localStoragePlugin]
})// Pinia
getters: {
activeHighPriorityTodos() {
const active = this.activeTodos // 他のゲッターを呼び出し
return active.filter(todo => todo.priority === 'high')
},
activeTodos() {
return this.todos.filter(todo => !todo.completed)
}
}// Vuex
getters: {
getTodoById: state => id => {
return state.todos.find(todo => todo.id === id)
}
}
// 使用例
this.$store.getters.getTodoById(123)// Pinia
getters: {
getItemByKey: state => (key, value) => {
return state.items.find(item => item[key] === value)
}
}
// 使用例
const user = userStore.getItemByKey('email', 'test@example.com')mutations: {
updateUser(state, payload) {
const { id, data } = payload
const user = state.users.find(u => u.id === id)
if (user) {
Object.assign(user, data)
}
}
}// Vuex
mutations: {
updateNestedProp(state, { path, value }) {
const keys = path.split('.')
const lastKey = keys.pop()
const target = keys.reduce((obj, key) => obj[key], state)
Vue.set(target, lastKey, value)
}
}mutations: {
updateArrayItem(state, { index, newItem }) {
Vue.set(state.items, index, { ...state.items[index], ...newItem })
}
}actions: {
async fetchDataSequentially({ commit }) {
await commit('setLoading', true)
const user = await fetchUser()
commit('setUser', user)
const posts = await fetchPosts(user.id)
commit('setPosts', posts)
commit('setLoading', false)
}
}actions: {
async fetchAllData({ commit }) {
const [users, posts] = await Promise.all([
fetchUsers(),
fetchPosts()
])
commit('setUsers', users)
commit('setPosts', posts)
}
}actions: {
async initializeApp({ dispatch }) {
await dispatch('fetchUser')
await dispatch('fetchSettings')
dispatch('loadPreferences')
}
}actions: {
async fetchData({ commit }) {
try {
commit('setLoading', true)
const data = await api.fetchData()
commit('setData', data)
return data
} catch (error) {
commit('setError', error.message)
throw error
} finally {
commit('setLoading', false)
}
}
}const loggerPlugin = store => {
store.subscribe((mutation, state) => {
console.log('Mutation:', mutation.type)
console.log('Payload:', mutation.payload)
console.log('Next State:', state)
})
}
const store = createStore({
// ...
plugins: [loggerPlugin]
})const piniaPersist = ({ store }) => {
const key = `pinia-${store.$id}`
const savedState = localStorage.getItem(key)
if (savedState) {
store.$patch(JSON.parse(savedState))
}
store.$subscribe((mutation, state) => {
localStorage.setItem(key, JSON.stringify(state))
})
}
const pinia = createPinia()
pinia.use(piniaPersist)// Vuex
const store = createStore({
// ...
plugins: [createLogger()]
})
// Pinia (デバッグ用)
import { PiniaUndo } from 'pinia-undo'
const pinia = createPinia()
pinia.use(PiniaUndo)// stores/
// ├── auth/
// ├── products/
// ├── cart/
// └── index.js
// stores/products/state.js
export default () => ({
items: [],
currentProduct: null,
loading: false
})
// stores/products/actions.js
export const actions = {
async loadProducts({ commit }) {
commit('SET_LOADING', true)
const products = await api.fetchProducts()
commit('SET_ITEMS', products)
commit('SET_LOADING', false)
}
}// Nuxt.jsのVuexストア例
// store/index.js
export const state = () => ({
loadedData: null
})
export const actions = {
async nuxtServerInit({ commit }, { req }) {
const data = await fetchInitialData(req)
commit('SET_DATA', data)
}
}
// Pinia SSR例
export default defineNuxtPlugin((nuxtApp) => {
nuxtApp.hook('app:created', async () => {
const store = useStore()
await store.fetchServerData()
})
})// Vuexストアのテスト例
import store from '@/store'
describe('counter store', () => {
beforeEach(() => {
store.commit('reset')
})
it('increments count', () => {
store.commit('increment')
expect(store.state.count).toBe(1)
})
it('async action', async () => {
await store.dispatch('fetchData')
expect(store.state.data).not.toBeNull()
})
})
// Piniaテスト例
import { useCounterStore } from '@/stores/counter'
import { setActivePinia, createPinia } from 'pinia'
describe('Counter Store', () => {
beforeEach(() => {
setActivePinia(createPinia())
})
it('increments', () => {
const counter = useCounterStore()
counter.increment()
expect(counter.count).toBe(1)
})
})interface UserState {
users: User[]
currentUser: User | null
loading: boolean
}
export const useUserStore = defineStore('user', {
state: (): UserState => ({
users: [],
currentUser: null,
loading: false
}),
getters: {
activeUsers: (state) => state.users.filter(u => u.isActive)
},
actions: {
async fetchUsers(): Promise {
this.loading = true
try {
this.users = await userService.getAll()
} finally {
this.loading = false
}
}
}
}) // repositories/ProductRepository.js
export default {
async getAll() {
const response = await axios.get('/products')
return response.data
},
async getById(id) {
const response = await axios.get(`/products/${id}`)
return response.data
}
}
// store/modules/products.js
import ProductRepository from '@/repositories/ProductRepository'
const actions = {
async loadProducts({ commit }) {
const products = await ProductRepository.getAll()
commit('SET_PRODUCTS', products)
}
}この演習セットは、Vuex/Piniaの状態管理を体系的に学ぶために設計されています。初級問題で基本概念を理解し、中級問題で実践的なスキルを習得し、上級問題でプロダクションレベルの設計パターンを学べる構成になっています。各解答には実際のプロジェクトで活用できる実用的なコード例を示しており、状態管理のベストプラクティスを習得するのに役立ちます。