
JFrameとJPanelの組み合わせ(基本コンポーネントの拡張)
JFrameに直接コンポーネントを追加するだけでなく、JPanelを活用することでより柔軟なレイアウトが可能になります。JPanelはコンポーネントをグループ化 […]
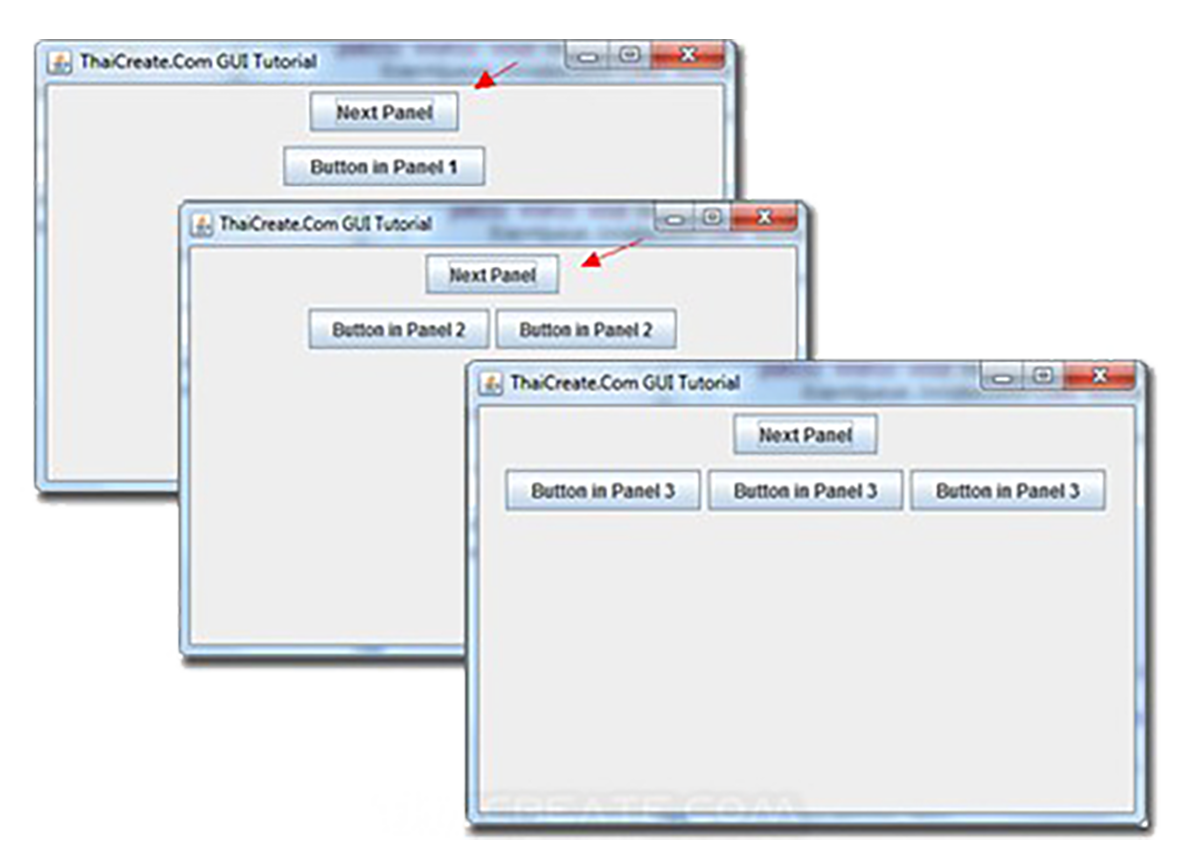
これまで学んだSwingの知識を統合し、複数画面を持つ本格的なアプリケーションを開発する方法を解説します。カードレイアウトを使用した画面遷移、データの受け渡し、アプリケーションのアーキテクチャ設計など、実践的な開発手法を紹介します。
import javax.swing.*;
import java.awt.*;
import java.awt.event.ActionEvent;
public class MultiScreenApp {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SwingUtilities.invokeLater(() -> {
JFrame frame = new JFrame("複数画面アプリケーション");
frame.setSize(800, 600);
frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
// カードレイアウトの設定
CardLayout cardLayout = new CardLayout();
JPanel mainPanel = new JPanel(cardLayout);
// 各画面の作成
MainMenuPanel mainMenu = new MainMenuPanel(cardLayout, mainPanel);
LoginPanel loginPanel = new LoginPanel(cardLayout, mainPanel);
DashboardPanel dashboardPanel = new DashboardPanel(cardLayout, mainPanel);
// 画面をカードとして追加
mainPanel.add(mainMenu, "MainMenu");
mainPanel.add(loginPanel, "Login");
mainPanel.add(dashboardPanel, "Dashboard");
// 最初の画面を表示
cardLayout.show(mainPanel, "MainMenu");
frame.add(mainPanel);
frame.setVisible(true);
});
}
}
// メインメニュー画面
class MainMenuPanel extends JPanel {
public MainMenuPanel(CardLayout cardLayout, JPanel parent) {
setLayout(new BorderLayout());
JLabel titleLabel = new JLabel("メインメニュー", SwingConstants.CENTER);
titleLabel.setFont(new Font("Meiryo", Font.BOLD, 24));
JPanel buttonPanel = new JPanel(new GridLayout(3, 1, 10, 10));
JButton loginButton = new JButton("ログイン");
loginButton.addActionListener(e -> cardLayout.show(parent, "Login"));
JButton exitButton = new JButton("終了");
exitButton.addActionListener(e -> System.exit(0));
buttonPanel.add(loginButton);
buttonPanel.add(new JButton("設定")); // 仮のボタン
buttonPanel.add(exitButton);
add(titleLabel, BorderLayout.NORTH);
add(buttonPanel, BorderLayout.CENTER);
}
}
// ログイン画面
class LoginPanel extends JPanel {
public LoginPanel(CardLayout cardLayout, JPanel parent) {
setLayout(new GridBagLayout());
GridBagConstraints gbc = new GridBagConstraints();
gbc.insets = new Insets(5, 5, 5, 5);
gbc.fill = GridBagConstraints.HORIZONTAL;
JLabel titleLabel = new JLabel("ログイン", SwingConstants.CENTER);
titleLabel.setFont(new Font("Meiryo", Font.BOLD, 20));
JTextField usernameField = new JTextField(15);
JPasswordField passwordField = new JPasswordField(15);
JButton loginButton = new JButton("ログイン");
JButton backButton = new JButton("戻る");
// レイアウト配置
gbc.gridwidth = 2;
gbc.gridx = 0;
gbc.gridy = 0;
add(titleLabel, gbc);
gbc.gridwidth = 1;
gbc.gridy = 1;
add(new JLabel("ユーザー名:"), gbc);
gbc.gridx = 1;
add(usernameField, gbc);
gbc.gridx = 0;
gbc.gridy = 2;
add(new JLabel("パスワード:"), gbc);
gbc.gridx = 1;
add(passwordField, gbc);
gbc.gridy = 3;
gbc.gridx = 0;
add(backButton, gbc);
gbc.gridx = 1;
add(loginButton, gbc);
// イベント処理
backButton.addActionListener(e -> cardLayout.show(parent, "MainMenu"));
loginButton.addActionListener(e -> {
// 簡易認証
String username = usernameField.getText();
char[] password = passwordField.getPassword();
if (username.equals("admin") && new String(password).equals("password")) {
cardLayout.show(parent, "Dashboard");
} else {
JOptionPane.showMessageDialog(this,
"ユーザー名またはパスワードが不正です",
"エラー",
JOptionPane.ERROR_MESSAGE);
}
});
}
}
// ダッシュボード画面
class DashboardPanel extends JPanel {
public DashboardPanel(CardLayout cardLayout, JPanel parent) {
setLayout(new BorderLayout());
JLabel welcomeLabel = new JLabel("ダッシュボード", SwingConstants.CENTER);
welcomeLabel.setFont(new Font("Meiryo", Font.BOLD, 24));
JButton logoutButton = new JButton("ログアウト");
logoutButton.addActionListener(e -> cardLayout.show(parent, "MainMenu"));
// タブ付きパネル
JTabbedPane tabbedPane = new JTabbedPane();
// タブ1: ユーザー情報
JPanel userPanel = new JPanel(new GridLayout(0, 1, 10, 10));
userPanel.add(new JLabel("名前: 山田太郎"));
userPanel.add(new JLabel("メール: yamada@example.com"));
userPanel.add(new JLabel("最終ログイン: 2023-11-15"));
// タブ2: 設定
JPanel settingsPanel = new JPanel();
settingsPanel.add(new JCheckBox("ダークモード"));
settingsPanel.add(new JCheckBox("通知を有効にする"));
tabbedPane.addTab("プロファイル", userPanel);
tabbedPane.addTab("設定", settingsPanel);
add(welcomeLabel, BorderLayout.NORTH);
add(tabbedPane, BorderLayout.CENTER);
add(logoutButton, BorderLayout.SOUTH);
}
}複数画面でデータを共有するための状態管理クラスを導入します。
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
public class AppState {
private static AppState instance;
private Map state;
private AppState() {
state = new HashMap<>();
}
public static synchronized AppState getInstance() {
if (instance == null) {
instance = new AppState();
}
return instance;
}
public void put(String key, Object value) {
state.put(key, value);
}
public Object get(String key) {
return state.get(key);
}
public void remove(String key) {
state.remove(key);
}
public void clear() {
state.clear();
}
}
// 使用例
AppState state = AppState.getInstance();
state.put("currentUser", "山田太郎");
String username = (String)state.get("currentUser"); 商品管理システムの例で、複数画面間でのデータ連携を実装します。
import javax.swing.*;
import java.awt.*;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
public class ProductManagementApp {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SwingUtilities.invokeLater(() -> {
// サンプルデータ
List products = new ArrayList<>();
products.add(new Product("ノートPC", 120000, 10));
products.add(new Product("スマートフォン", 80000, 15));
JFrame frame = new JFrame("商品管理システム");
frame.setSize(900, 600);
frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
CardLayout cardLayout = new CardLayout();
JPanel mainPanel = new JPanel(cardLayout);
// 商品リスト画面
ProductListPanel listPanel = new ProductListPanel(products, cardLayout, mainPanel);
// 商品詳細画面
ProductDetailPanel detailPanel = new ProductDetailPanel(cardLayout, mainPanel);
// 商品追加画面
ProductAddPanel addPanel = new ProductAddPanel(cardLayout, mainPanel, products, listPanel);
mainPanel.add(listPanel, "List");
mainPanel.add(detailPanel, "Detail");
mainPanel.add(addPanel, "Add");
frame.add(mainPanel);
frame.setVisible(true);
});
}
}
class Product {
private String name;
private int price;
private int stock;
public Product(String name, int price, int stock) {
this.name = name;
this.price = price;
this.stock = stock;
}
// getters and setters...
}
class ProductListPanel extends JPanel {
private JTable table;
private ProductTableModel model;
public ProductListPanel(List products, CardLayout cardLayout, JPanel parent) {
setLayout(new BorderLayout());
// テーブルモデルの作成
model = new ProductTableModel(products);
table = new JTable(model);
// テーブル選択時の処理
table.getSelectionModel().addListSelectionListener(e -> {
if (!e.getValueIsAdjusting()) {
int selectedRow = table.getSelectedRow();
if (selectedRow >= 0) {
Product selected = model.getProductAt(selectedRow);
AppState.getInstance().put("selectedProduct", selected);
cardLayout.show(parent, "Detail");
}
}
});
// ボタンパネル
JPanel buttonPanel = new JPanel(new FlowLayout(FlowLayout.RIGHT));
JButton addButton = new JButton("商品追加");
addButton.addActionListener(e -> cardLayout.show(parent, "Add"));
buttonPanel.add(addButton);
add(new JScrollPane(table), BorderLayout.CENTER);
add(buttonPanel, BorderLayout.SOUTH);
}
public void refreshTable() {
model.fireTableDataChanged();
}
}
class ProductDetailPanel extends JPanel {
public ProductDetailPanel(CardLayout cardLayout, JPanel parent) {
setLayout(new BorderLayout());
JPanel detailPanel = new JPanel(new GridLayout(0, 1, 10, 10));
JLabel nameLabel = new JLabel();
JLabel priceLabel = new JLabel();
JLabel stockLabel = new JLabel();
detailPanel.add(new JLabel("商品詳細", SwingConstants.CENTER));
detailPanel.add(new JSeparator());
detailPanel.add(new JLabel("商品名:"));
detailPanel.add(nameLabel);
detailPanel.add(new JLabel("価格:"));
detailPanel.add(priceLabel);
detailPanel.add(new JLabel("在庫数:"));
detailPanel.add(stockLabel);
JButton backButton = new JButton("戻る");
backButton.addActionListener(e -> {
table.clearSelection();
cardLayout.show(parent, "List");
});
// 状態の監視と表示更新
AppState.getInstance().addPropertyChangeListener(evt -> {
if ("selectedProduct".equals(evt.getPropertyName())) {
Product product = (Product)evt.getNewValue();
nameLabel.setText(product.getName());
priceLabel.setText(String.format("%,d円", product.getPrice()));
stockLabel.setText(String.valueOf(product.getStock()));
}
});
add(detailPanel, BorderLayout.CENTER);
add(backButton, BorderLayout.SOUTH);
}
}
class ProductAddPanel extends JPanel {
public ProductAddPanel(CardLayout cardLayout, JPanel parent,
List products, ProductListPanel listPanel) {
setLayout(new GridBagLayout());
GridBagConstraints gbc = new GridBagConstraints();
gbc.insets = new Insets(5, 5, 5, 5);
gbc.fill = GridBagConstraints.HORIZONTAL;
JTextField nameField = new JTextField(20);
JSpinner priceSpinner = new JSpinner(new SpinnerNumberModel(0, 0, 1000000, 100));
JSpinner stockSpinner = new JSpinner(new SpinnerNumberModel(0, 0, 1000, 1));
JButton saveButton = new JButton("保存");
JButton cancelButton = new JButton("キャンセル");
// レイアウト配置
gbc.gridwidth = 2;
gbc.gridx = 0;
gbc.gridy = 0;
add(new JLabel("新規商品追加", SwingConstants.CENTER), gbc);
gbc.gridwidth = 1;
gbc.gridy = 1;
add(new JLabel("商品名:"), gbc);
gbc.gridx = 1;
add(nameField, gbc);
gbc.gridx = 0;
gbc.gridy = 2;
add(new JLabel("価格:"), gbc);
gbc.gridx = 1;
add(priceSpinner, gbc);
gbc.gridx = 0;
gbc.gridy = 3;
add(new JLabel("在庫数:"), gbc);
gbc.gridx = 1;
add(stockSpinner, gbc);
gbc.gridy = 4;
gbc.gridx = 0;
add(cancelButton, gbc);
gbc.gridx = 1;
add(saveButton, gbc);
// イベント処理
cancelButton.addActionListener(e -> {
nameField.setText("");
priceSpinner.setValue(0);
stockSpinner.setValue(0);
cardLayout.show(parent, "List");
});
saveButton.addActionListener(e -> {
String name = nameField.getText();
int price = (Integer)priceSpinner.getValue();
int stock = (Integer)stockSpinner.getValue();
if (!name.isEmpty() && price > 0) {
products.add(new Product(name, price, stock));
listPanel.refreshTable();
nameField.setText("");
priceSpinner.setValue(0);
stockSpinner.setValue(0);
cardLayout.show(parent, "List");
} else {
JOptionPane.showMessageDialog(this,
"商品名と価格を正しく入力してください",
"入力エラー",
JOptionPane.WARNING_MESSAGE);
}
});
}
} // 国際化対応の例
ResourceBundle bundle = ResourceBundle.getBundle("messages");
JLabel label = new JLabel(bundle.getString("login.title"));
JButton button = new JButton(bundle.getString("login.button"));このような設計パターンを適用することで、保守性の高い複数画面アプリケーションを開発できます。次に進む「Swingアプリケーションのデプロイ」では、完成したアプリケーションを配布可能な形式にパッケージ化する方法を学びます。