
JFrameとJPanelの組み合わせ(基本コンポーネントの拡張)
JFrameに直接コンポーネントを追加するだけでなく、JPanelを活用することでより柔軟なレイアウトが可能になります。JPanelはコンポーネントをグループ化 […]
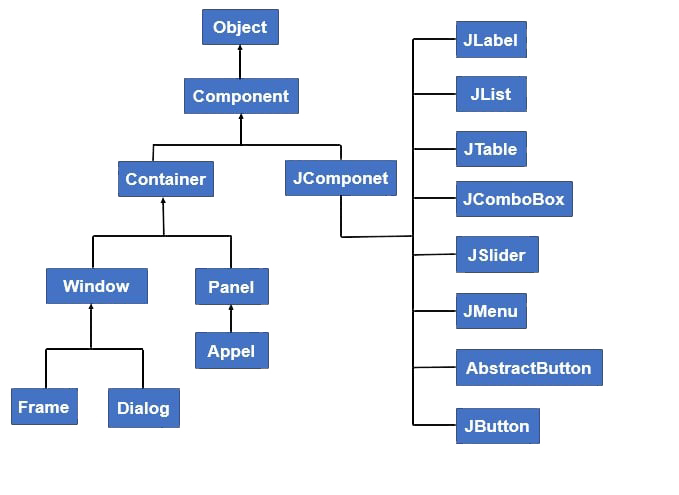
Swingアプリケーションで標準のJOptionPaneでは実現できない複雑なダイアログが必要な場合、JDialogクラスを使用して完全にカスタマイズ可能なダイアログを作成できます。JDialogは独立したウィンドウとして動作し、モーダルまたはモードレスで使用できます。
import javax.swing.*;
import java.awt.*;
import java.awt.event.ActionEvent;
public class BasicCustomDialog {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SwingUtilities.invokeLater(() -> {
JFrame frame = new JFrame("メインウィンドウ");
frame.setSize(500, 400);
frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
JButton showDialogButton = new JButton("ダイアログを表示");
showDialogButton.addActionListener(e -> {
// ダイアログの作成(モーダル)
JDialog dialog = new JDialog(frame, "カスタムダイアログ", true);
dialog.setSize(300, 200);
dialog.setLayout(new BorderLayout());
// コンテンツの追加
dialog.add(new JLabel("これはカスタムダイアログです", SwingConstants.CENTER), BorderLayout.CENTER);
// 閉じるボタン
JButton closeButton = new JButton("閉じる");
closeButton.addActionListener(ev -> dialog.dispose());
JPanel buttonPanel = new JPanel();
buttonPanel.add(closeButton);
dialog.add(buttonPanel, BorderLayout.SOUTH);
// ダイアログを中央に表示
dialog.setLocationRelativeTo(frame);
dialog.setVisible(true);
});
frame.add(showDialogButton);
frame.setVisible(true);
});
}
}import javax.swing.*;
import java.awt.*;
import java.awt.event.ActionEvent;
public class ModalDialogExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SwingUtilities.invokeLater(() -> {
JFrame frame = new JFrame("データ受け渡し例");
frame.setSize(500, 400);
frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
JLabel resultLabel = new JLabel(" ", SwingConstants.CENTER);
resultLabel.setFont(new Font("Meiryo", Font.BOLD, 16));
JButton showDialogButton = new JButton("ログインダイアログを表示");
showDialogButton.addActionListener(e -> {
LoginDialog loginDialog = new LoginDialog(frame);
loginDialog.setVisible(true); // モーダルダイアログ表示
// ダイアログが閉じられた後に結果を取得
if (loginDialog.isSuccess()) {
resultLabel.setText("ログイン成功: " + loginDialog.getUsername());
} else {
resultLabel.setText("ログインがキャンセルされました");
}
});
frame.add(showDialogButton, BorderLayout.NORTH);
frame.add(resultLabel, BorderLayout.CENTER);
frame.setVisible(true);
});
}
}
class LoginDialog extends JDialog {
private JTextField usernameField;
private JPasswordField passwordField;
private boolean success = false;
public LoginDialog(JFrame parent) {
super(parent, "ログイン", true); // モーダルダイアログ
setSize(300, 200);
setLayout(new GridLayout(3, 2, 10, 10));
setLocationRelativeTo(parent);
// コンポーネントの作成
add(new JLabel("ユーザー名:"));
usernameField = new JTextField();
add(usernameField);
add(new JLabel("パスワード:"));
passwordField = new JPasswordField();
add(passwordField);
// ボタンパネル
JButton loginButton = new JButton("ログイン");
loginButton.addActionListener(e -> {
if (!usernameField.getText().isEmpty() && passwordField.getPassword().length > 0) {
success = true;
dispose();
} else {
JOptionPane.showMessageDialog(this,
"ユーザー名とパスワードを入力してください",
"エラー",
JOptionPane.ERROR_MESSAGE);
}
});
JButton cancelButton = new JButton("キャンセル");
cancelButton.addActionListener(e -> dispose());
JPanel buttonPanel = new JPanel();
buttonPanel.add(loginButton);
buttonPanel.add(cancelButton);
add(new JLabel()); // 空のセル
add(buttonPanel);
// エンターキーでログイン
getRootPane().setDefaultButton(loginButton);
}
public boolean isSuccess() {
return success;
}
public String getUsername() {
return usernameField.getText();
}
}import javax.swing.*;
import java.awt.*;
import java.awt.event.ActionEvent;
public class ComplexDialogExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SwingUtilities.invokeLater(() -> {
JFrame frame = new JFrame("複雑なダイアログ例");
frame.setSize(600, 400);
frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
JButton showDialogButton = new JButton("設定ダイアログを表示");
showDialogButton.addActionListener(e -> {
SettingsDialog dialog = new SettingsDialog(frame);
dialog.setVisible(true);
});
frame.add(showDialogButton);
frame.setVisible(true);
});
}
}
class SettingsDialog extends JDialog {
public SettingsDialog(JFrame parent) {
super(parent, "アプリケーション設定", true);
setSize(450, 350);
setLocationRelativeTo(parent);
// メインパネル
JPanel mainPanel = new JPanel(new BorderLayout(10, 10));
mainPanel.setBorder(BorderFactory.createEmptyBorder(10, 10, 10, 10));
// タブペイン
JTabbedPane tabbedPane = new JTabbedPane();
// 一般設定タブ
JPanel generalPanel = new JPanel(new GridLayout(0, 1, 5, 5));
generalPanel.add(new JCheckBox("起動時に最新ニュースをチェック"));
generalPanel.add(new JCheckBox("自動更新を有効にする"));
JPanel languagePanel = new JPanel(new FlowLayout(FlowLayout.LEFT));
languagePanel.add(new JLabel("言語:"));
languagePanel.add(new JComboBox<>(new String[]{"日本語", "英語", "中国語"}));
generalPanel.add(languagePanel);
tabbedPane.addTab("一般", generalPanel);
// 表示設定タブ
JPanel appearancePanel = new JPanel(new GridLayout(0, 1, 5, 5));
ButtonGroup themeGroup = new ButtonGroup();
JRadioButton lightTheme = new JRadioButton("ライトテーマ", true);
JRadioButton darkTheme = new JRadioButton("ダークテーマ");
themeGroup.add(lightTheme);
themeGroup.add(darkTheme);
appearancePanel.add(new JLabel("テーマ:"));
appearancePanel.add(lightTheme);
appearancePanel.add(darkTheme);
JPanel fontSizePanel = new JPanel(new FlowLayout(FlowLayout.LEFT));
fontSizePanel.add(new JLabel("フォントサイズ:"));
fontSizePanel.add(new JSpinner(new SpinnerNumberModel(12, 8, 24, 1)));
appearancePanel.add(fontSizePanel);
tabbedPane.addTab("表示", appearancePanel);
// ボタンパネル
JPanel buttonPanel = new JPanel(new FlowLayout(FlowLayout.RIGHT));
JButton okButton = new JButton("OK");
okButton.addActionListener(e -> dispose());
JButton cancelButton = new JButton("キャンセル");
cancelButton.addActionListener(e -> dispose());
JButton applyButton = new JButton("適用");
applyButton.addActionListener(e -> {
JOptionPane.showMessageDialog(this, "設定が適用されました");
});
buttonPanel.add(applyButton);
buttonPanel.add(cancelButton);
buttonPanel.add(okButton);
// レイアウトの組み立て
mainPanel.add(tabbedPane, BorderLayout.CENTER);
mainPanel.add(buttonPanel, BorderLayout.SOUTH);
add(mainPanel);
// デフォルトボタンの設定
getRootPane().setDefaultButton(okButton);
}
}import javax.swing.*;
import java.awt.*;
import java.awt.event.WindowAdapter;
import java.awt.event.WindowEvent;
public class DialogLifecycleExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SwingUtilities.invokeLater(() -> {
JFrame frame = new JFrame("ダイアログライフサイクル例");
frame.setSize(500, 400);
frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
JTextArea logArea = new JTextArea();
logArea.setEditable(false);
JButton showDialogButton = new JButton("ライフサイクルダイアログを表示");
showDialogButton.addActionListener(e -> {
JDialog dialog = new JDialog(frame, "ライフサイクルダイアログ", false); // モードレス
dialog.setSize(300, 200);
// ウィンドウリスナーの追加
dialog.addWindowListener(new WindowAdapter() {
@Override
public void windowOpened(WindowEvent e) {
logArea.append("ダイアログが開かれました\n");
}
@Override
public void windowClosing(WindowEvent e) {
logArea.append("ダイアログが閉じられようとしています\n");
}
@Override
public void windowClosed(WindowEvent e) {
logArea.append("ダイアログが閉じられました\n");
}
@Override
public void windowActivated(WindowEvent e) {
logArea.append("ダイアログがアクティブになりました\n");
}
@Override
public void windowDeactivated(WindowEvent e) {
logArea.append("ダイアログが非アクティブになりました\n");
}
});
dialog.setVisible(true);
});
frame.add(showDialogButton, BorderLayout.NORTH);
frame.add(new JScrollPane(logArea), BorderLayout.CENTER);
frame.setVisible(true);
});
}
}import javax.swing.*;
import java.awt.*;
import java.awt.event.ActionEvent;
public class GradientDialogExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SwingUtilities.invokeLater(() -> {
JFrame frame = new JFrame("グラデーションダイアログ例");
frame.setSize(600, 400);
frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
JButton showDialogButton = new JButton("グラデーションダイアログを表示");
showDialogButton.addActionListener(e -> {
GradientDialog dialog = new GradientDialog(frame);
dialog.setVisible(true);
});
frame.add(showDialogButton);
frame.setVisible(true);
});
}
}
class GradientDialog extends JDialog {
public GradientDialog(JFrame parent) {
super(parent, "グラデーションダイアログ", true);
setSize(400, 300);
setLocationRelativeTo(parent);
setUndecorated(true); // タイトルバーを非表示
// カスタムコンテンツペイン
JPanel contentPane = new JPanel(new BorderLayout()) {
@Override
protected void paintComponent(Graphics g) {
super.paintComponent(g);
Graphics2D g2d = (Graphics2D)g;
// グラデーションの作成
GradientPaint gradient = new GradientPaint(
0, 0, new Color(70, 130, 180),
getWidth(), getHeight(), new Color(135, 206, 250));
g2d.setPaint(gradient);
g2d.fillRect(0, 0, getWidth(), getHeight());
}
};
contentPane.setBorder(BorderFactory.createLineBorder(Color.WHITE, 2));
// ダイアログコンテンツ
JLabel titleLabel = new JLabel("カスタムグラデーションダイアログ", SwingConstants.CENTER);
titleLabel.setFont(new Font("Meiryo", Font.BOLD, 18));
titleLabel.setForeground(Color.WHITE);
JButton closeButton = new JButton("閉じる");
closeButton.addActionListener(e -> dispose());
closeButton.setContentAreaFilled(false);
closeButton.setForeground(Color.WHITE);
closeButton.setBorder(BorderFactory.createLineBorder(Color.WHITE));
// ドラッグで移動可能にする
MouseAdapter ma = new MouseAdapter() {
private Point initialClick;
@Override
public void mousePressed(MouseEvent e) {
initialClick = e.getPoint();
}
@Override
public void mouseDragged(MouseEvent e) {
int thisX = getLocation().x;
int thisY = getLocation().y;
int xMoved = e.getX() - initialClick.x;
int yMoved = e.getY() - initialClick.y;
setLocation(thisX + xMoved, thisY + yMoved);
}
};
contentPane.addMouseListener(ma);
contentPane.addMouseMotionListener(ma);
// レイアウト
contentPane.add(titleLabel, BorderLayout.CENTER);
contentPane.add(closeButton, BorderLayout.SOUTH);
setContentPane(contentPane);
}
}dispose()で解放 getRootPane().setDefaultButton(defaultButton);// 国際化対応の例
ResourceBundle bundle = ResourceBundle.getBundle("DialogResources");
setTitle(bundle.getString("dialog.title"));
JLabel label = new JLabel(bundle.getString("dialog.message"));カスタムダイアログを適切に設計することで、アプリケーションのユーザビリティを大幅に向上させることができます。次に学ぶ「Swingアプリケーションのアーキテクチャ」では、これらのコンポーネントを効果的に組み合わせる設計パターンを解説します。