
JFrameとJPanelの組み合わせ(基本コンポーネントの拡張)
JFrameに直接コンポーネントを追加するだけでなく、JPanelを活用することでより柔軟なレイアウトが可能になります。JPanelはコンポーネントをグループ化 […]
Swingのレイアウトマネージャーは、コンポーネントのサイズと位置を自動的に管理する仕組みです。適切なレイアウトマネージャーを使用することで、異なる画面サイズや解像度でも適切に表示されるGUIを作成できます。
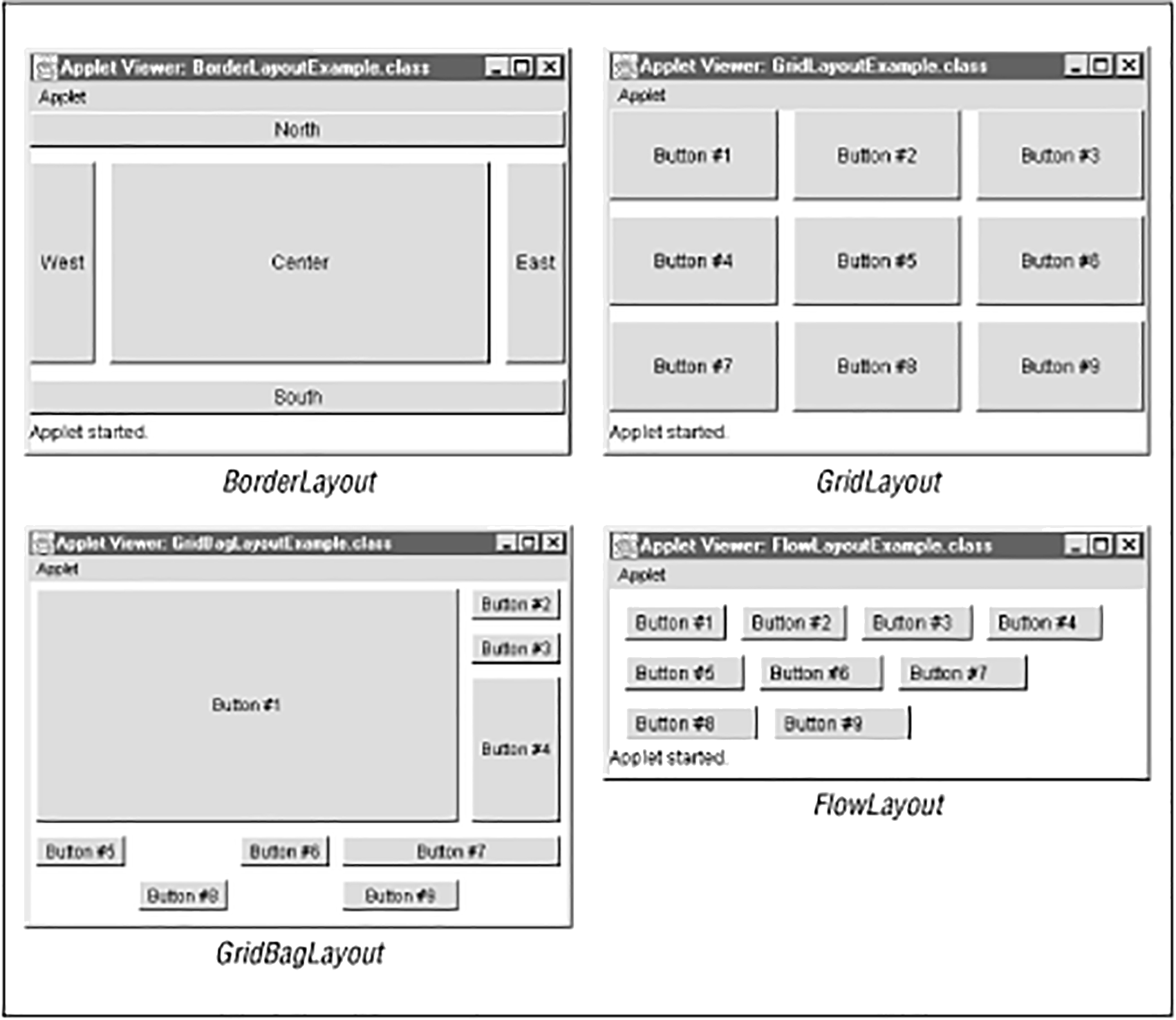
特徴:
import javax.swing.*;
import java.awt.*;
public class BorderLayoutExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SwingUtilities.invokeLater(() -> {
JFrame frame = new JFrame("BorderLayoutの例");
frame.setSize(400, 300);
frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
// BorderLayoutの設定(水平間隔5、垂直間隔5)
frame.setLayout(new BorderLayout(5, 5));
// 各領域にコンポーネントを追加
frame.add(new JButton("北"), BorderLayout.NORTH);
frame.add(new JButton("南"), BorderLayout.SOUTH);
frame.add(new JButton("東"), BorderLayout.EAST);
frame.add(new JButton("西"), BorderLayout.WEST);
frame.add(new JButton("中央"), BorderLayout.CENTER);
frame.setVisible(true);
});
}
}特徴:
import javax.swing.*;
import java.awt.*;
public class FlowLayoutExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SwingUtilities.invokeLater(() -> {
JFrame frame = new JFrame("FlowLayoutの例");
frame.setSize(400, 300);
frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
// FlowLayoutの設定(中央揃え、水平間隔10、垂直間隔20)
frame.setLayout(new FlowLayout(FlowLayout.CENTER, 10, 20));
// 複数のボタンを追加
for (int i = 1; i <= 10; i++) {
frame.add(new JButton("ボタン " + i));
}
frame.setVisible(true);
});
}
}特徴:
import javax.swing.*;
import java.awt.*;
public class GridLayoutExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SwingUtilities.invokeLater(() -> {
JFrame frame = new JFrame("GridLayoutの例");
frame.setSize(400, 300);
frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
// GridLayoutの設定(2行3列、水平間隔5、垂直間隔5)
frame.setLayout(new GridLayout(2, 3, 5, 5));
// 6つのボタンを追加
for (int i = 1; i <= 6; i++) {
frame.add(new JButton("ボタン " + i));
}
frame.setVisible(true);
});
}
}特徴:
import javax.swing.*;
import java.awt.*;
public class GridBagLayoutExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SwingUtilities.invokeLater(() -> {
JFrame frame = new JFrame("GridBagLayoutの例");
frame.setSize(500, 400);
frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
JPanel panel = new JPanel(new GridBagLayout());
GridBagConstraints gbc = new GridBagConstraints();
// 共通設定
gbc.fill = GridBagConstraints.HORIZONTAL;
gbc.insets = new Insets(5, 5, 5, 5); // マージン
// ラベル1 (0,0)
gbc.gridx = 0;
gbc.gridy = 0;
panel.add(new JLabel("名前:"), gbc);
// テキストフィールド1 (1,0)
gbc.gridx = 1;
gbc.gridwidth = 2; // 2列分占有
panel.add(new JTextField(20), gbc);
// ラベル2 (0,1)
gbc.gridx = 0;
gbc.gridy = 1;
gbc.gridwidth = 1; // リセット
panel.add(new JLabel("住所:"), gbc);
// テキストフィールド2 (1,1)
gbc.gridx = 1;
gbc.gridwidth = 2;
panel.add(new JTextField(20), gbc);
// ボタン1 (1,2)
gbc.gridx = 1;
gbc.gridy = 2;
gbc.gridwidth = 1;
gbc.weightx = 0.5; // 余白の分配
panel.add(new JButton("保存"), gbc);
// ボタン2 (2,2)
gbc.gridx = 2;
panel.add(new JButton("キャンセル"), gbc);
frame.add(panel);
frame.setVisible(true);
});
}
}| レイアウト | 適したケース | 不向きなケース |
|---|---|---|
| BorderLayout | メインウィンドウの基本構造 | 複雑な配置 |
| FlowLayout | ツールバーや単純なボタン群 | 精密な配置 |
| GridLayout | フォームや均等配置が必要な場合 | 柔軟なレイアウト |
| GridBagLayout | 複雑で精密なレイアウト | 簡単な配置 |
import javax.swing.*;
import java.awt.*;
public class CombinedLayoutExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SwingUtilities.invokeLater(() -> {
JFrame frame = new JFrame("レイアウト組み合わせ例");
frame.setSize(600, 400);
frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
// メインパネル(BorderLayout)
JPanel mainPanel = new JPanel(new BorderLayout(5, 5));
// ヘッダーパネル(NORTH - FlowLayout)
JPanel headerPanel = new JPanel(new FlowLayout(FlowLayout.CENTER));
headerPanel.add(new JLabel("アプリケーションタイトル"));
headerPanel.setBackground(new Color(220, 230, 240));
// サイドバーパネル(WEST - GridLayout)
JPanel sidePanel = new JPanel(new GridLayout(5, 1, 0, 10));
sidePanel.setBorder(BorderFactory.createEmptyBorder(10, 10, 10, 10));
sidePanel.add(new JButton("メニュー1"));
sidePanel.add(new JButton("メニュー2"));
sidePanel.add(new JButton("メニュー3"));
sidePanel.add(new JButton("メニュー4"));
sidePanel.add(new JButton("メニュー5"));
// コンテンツパネル(CENTER - GridBagLayout)
JPanel contentPanel = new JPanel(new GridBagLayout());
GridBagConstraints gbc = new GridBagConstraints();
gbc.insets = new Insets(5, 5, 5, 5);
gbc.fill = GridBagConstraints.HORIZONTAL;
gbc.gridx = 0; gbc.gridy = 0;
contentPanel.add(new JLabel("ユーザー名:"), gbc);
gbc.gridx = 1; gbc.gridwidth = 2;
contentPanel.add(new JTextField(20), gbc);
gbc.gridx = 0; gbc.gridy = 1; gbc.gridwidth = 1;
contentPanel.add(new JLabel("パスワード:"), gbc);
gbc.gridx = 1; gbc.gridwidth = 2;
contentPanel.add(new JPasswordField(20), gbc);
gbc.gridx = 1; gbc.gridy = 2;
contentPanel.add(new JButton("ログイン"), gbc);
gbc.gridx = 2;
contentPanel.add(new JButton("キャンセル"), gbc);
// メインパネルに追加
mainPanel.add(headerPanel, BorderLayout.NORTH);
mainPanel.add(sidePanel, BorderLayout.WEST);
mainPanel.add(contentPanel, BorderLayout.CENTER);
frame.add(mainPanel);
frame.setVisible(true);
});
}
}setBorderやEmptyBorderで適切な余白を確保// デバッグ用にコンポーネントに色を設定
panel.setBackground(Color.PINK);
button.setBackground(Color.CYAN);次の章では、これらのレイアウトに配置したコンポーネントに「イベント処理の基本(ActionListenerなど)」を追加して、インタラクティブなアプリケーションを作成する方法を学びます。